Datetime:2026-01-28
In the field of medical device manufacturing, the processing quality of precision components directly affects the diagnostic accuracy and treatment safety of the equipment. For example, the micro-clamping components in surgical instruments or fluid channel parts in laboratory analysis instruments require dimensional accuracy to be controlled at the micron level to ensure the stable operation of the equipment.
These components are core elements of medical devices, and the market demand continues to rise with the growth of the global healthcare industry. However, traditional milling methods often face bottlenecks such as low efficiency, unstable precision, and fragmented processes when dealing with complex profiles or parts with high precision requirements. How to overcome these common challenges and meet the strict processing standards for medical device components? Milling technology is the key to solving this dilemma.
Milling technology uses a digital control system (CNC) to control the spindle and table movements of the milling machine to achieve precise cutting and processing of parts. Its core components include the device, spindle system, feed system, worktable, and auxiliary parts. The device controls the spindle's rotation speed and direction, as well as the feed motion of the table along the X, Y, and Z axes, based on a pre-programmed program, to complete the milling process.
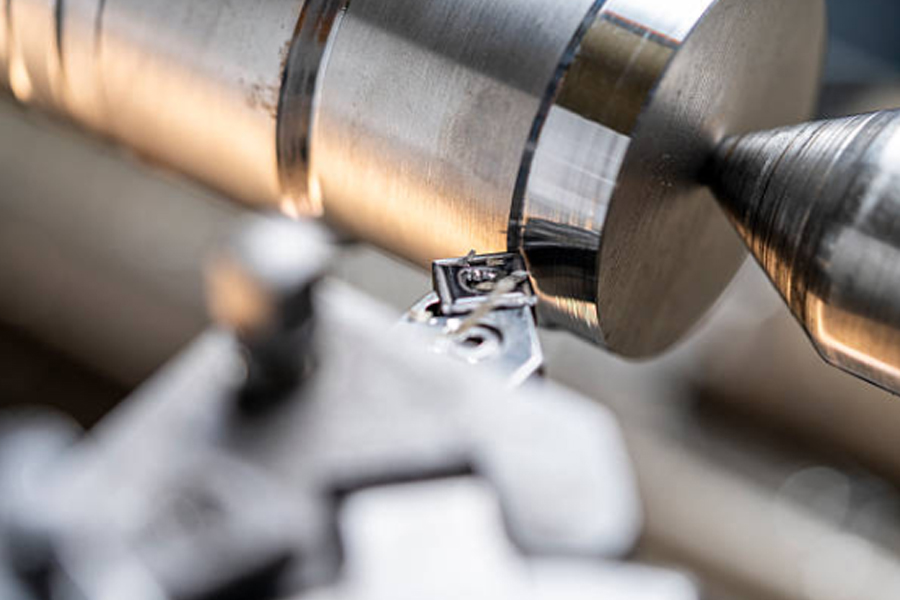

The machining center is an upgraded version of the milling machine, adding a tool library and automatic tool changer (ATC), allowing for automatic tool changes and reducing manual intervention. Some machining centers also come with an automatic indexing rotary table, allowing multiple surfaces to be processed after a single clamping of the workpiece, demonstrating the advantage of centralized processes.
Traditional milling relies on manual operation, and its precision is highly dependent on the operator's skill level. Tool changes are done manually, which is less efficient. For complex parts, traditional processing requires multiple clamping, which easily leads to cumulative errors and cannot meet the high precision requirements for medical device components.
In contrast, milling technology uses program control, achieving processing precision of ±0.005mm, with stable processing that is unaffected by human factors. The automatic tool changing function of the machining center enables continuous multi-process machining, reducing the number of clamping operations, minimizing errors, and shortening production cycles. For example, a medical component that requires multiple processes might take 3 hours with traditional processing, whereas the machining center can complete it in just 1 hour.
Milling technology is widely used in the processing of medical device components, life science parts, and high-end manufacturing. In medical device manufacturing, it is commonly used to make complex profile parts for surgical instruments (e.g., the jaws of hemostats), sample processing modules for laboratory equipment (e.g., high-precision hole location machining), and medical molds (e.g., syringe molds).
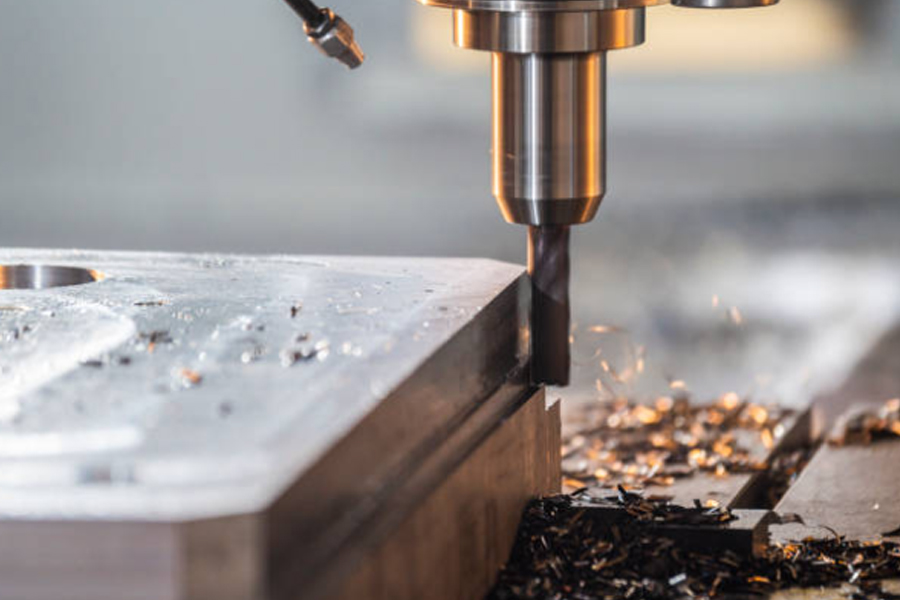

In the life sciences field, milling technology is used to process microfluidic chip molds, where micron-level channel structures require high-precision milling techniques. Furthermore, milling technology is also applied in aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and other fields, but its role in the medical industry is especially prominent due to the industry's strict quality requirements.
The core advantages of milling technology include high precision, high efficiency, and high adaptability. High precision is reflected in its ability to consistently control part dimensional errors, meeting the strict standards of the medical industry. High efficiency is derived from the centralized processes and automatic tool changing functionality, which reduces production time.
High adaptability is demonstrated by its ability to process complex profile parts, such as three-dimensional surfaces or irregular shapes. In terms of processing effects, milling technology reduces scrap rates, improves part consistency, and lowers labor costs. For example, after adopting milling technology, a medical device manufacturer reduced its scrap rate from 5% to 1%, while production efficiency increased by 40%.
Professional milling service providers, catering to the processing needs of medical device components, must be equipped with highly automated equipment. Their machining centers should feature advanced feed servo systems that enable multi-axis linkage and reduce manual intervention. Core components such as spindles and guide rails should be made from wear-resistant materials to ensure long-term stable operation and reduce maintenance costs.
Research and development teams continuously optimize machining processes, developing special cutting parameters for the medical industry's unique materials (e.g., titanium alloys, stainless steel) to improve processing efficiency and part quality. For example, after using professional milling services, a medical device manufacturer improved the processing precision of its surgical instrument parts by 20%, shortened production cycles by 30%, and effectively met the market's demand for high-quality components.
According to industry reports, the global medical device market is expected to reach $500 billion by 2025, driving the growth in demand for high-precision component processing. As a key machining technology, the market demand for milling technology will continue to grow at an annual rate of over 10%.
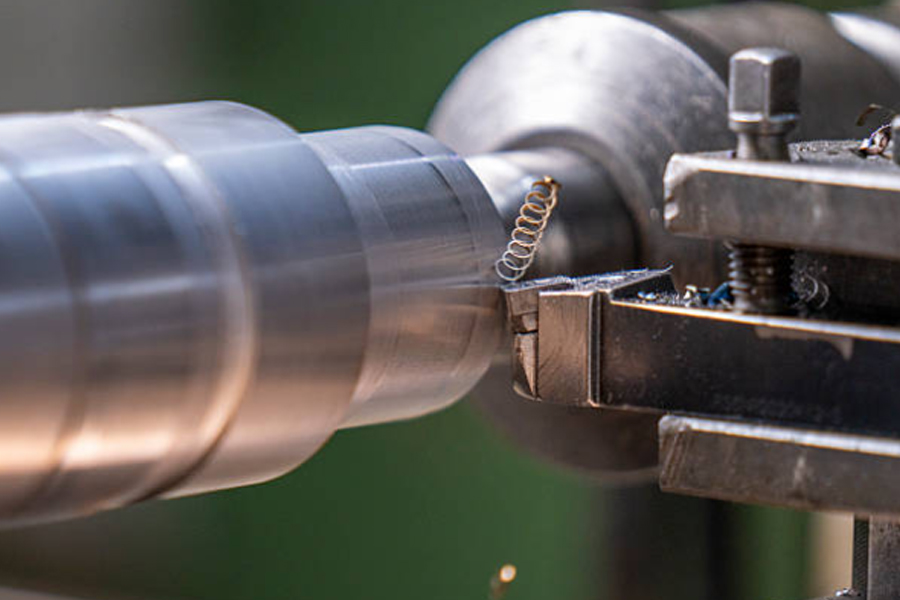
At the same time, with the advancement of smart manufacturing, milling equipment will evolve toward higher precision and greater intelligence, such as integrating AI technologies to optimize processing parameters, further enhancing processing efficiency and quality. In the future, milling technology will play an increasingly important role in the medical industry, becoming a core technology for high-end component processing.
When selecting a professional milling service provider, it is important to consider the automation level of their equipment, the durability of core components, their R&D capabilities, and their customer cases. High automation ensures processing stability, while durable core components reduce maintenance costs. A strong R&D team can optimize processes for special needs, and customer cases reflect the reliability of the service.
For example, a professional service provider's machining center is equipped with imported spindles with a lifespan of over 10 years. Additionally, their R&D team has more than 10 years of experience in medical industry processing and has provided services to several well-known medical device manufacturers.
Milling technology, with its characteristics of high precision and high efficiency, has become the core technology for processing medical device components. Choosing a service provider with professional expertise is the key to ensuring component quality and improving production efficiency. In the future, with technological advancements in the industry, milling technology will play a more important role in many high-end manufacturing fields.